How Brahmand Models and Stores Graph Data
Brahmand translates high-level Cypher DDL into ClickHouse tables.
Example
Section titled “Example”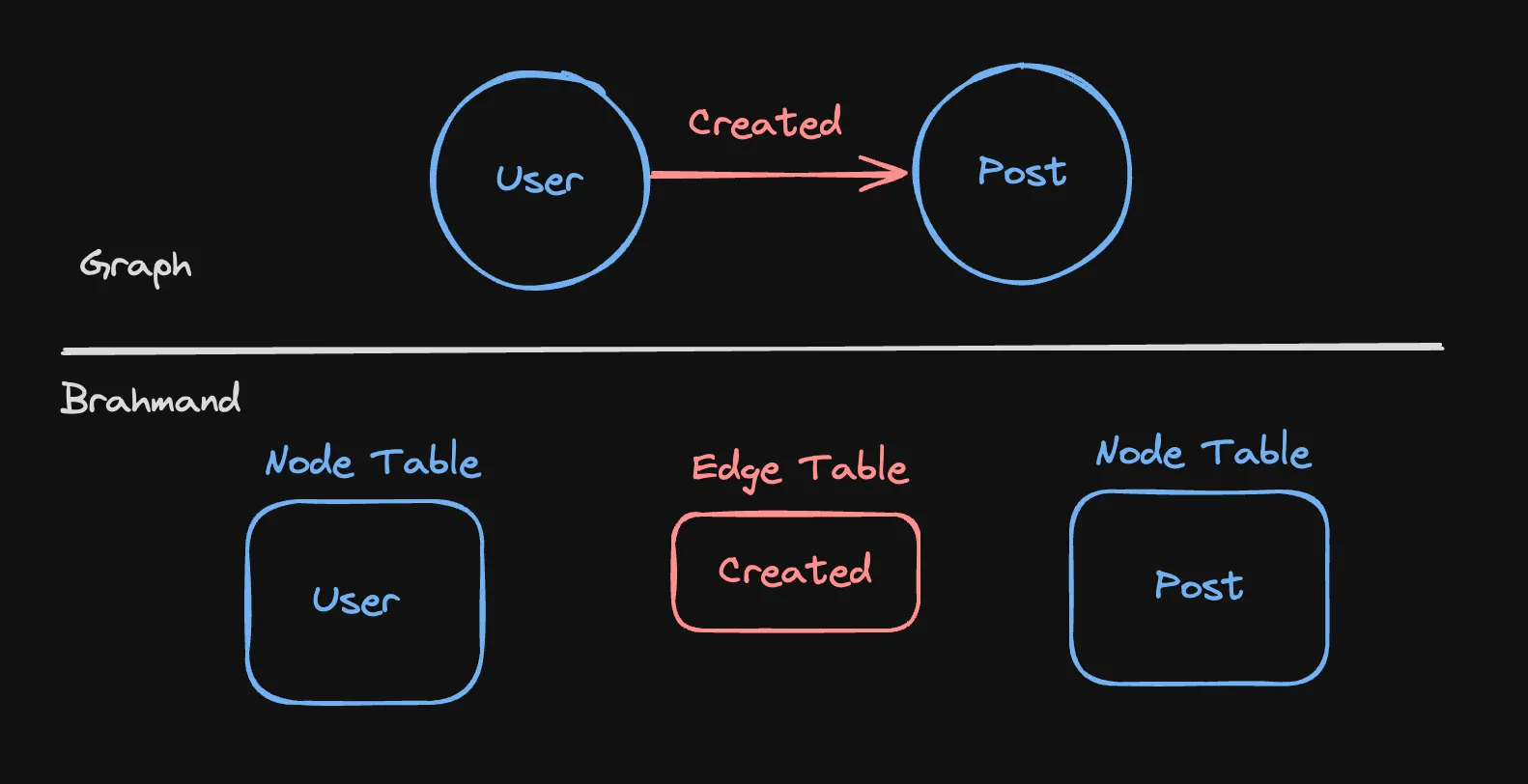
- Nodes:
User,Post - Relationship:
Created
Cypher DDL
Section titled “Cypher DDL”CREATE NODE TABLE User( UserId UInt64, Reputation String, <!-- other columns --> NODE ID(UserId), PRIMARY KEY(Reputation, UserId));
CREATE NODE TABLE Post( PostID UInt64, PostTypeId Int8, <!-- other columns --> NODE id(PostID), PRIMARY KEY(PostTypeId, PostID));
CREATE REL TABLE CREATED(From User To Post);ClickHouse Translation
Section titled “ClickHouse Translation”-- node UserCREATE TABLE User( userId UInt64, Reputation String, ...) ENGINE = MergeTreeORDER BY(Reputation, userId);
-- node PostCREATE TABLE Post( postId UInt64, PostTypeId Int8, ...) ENGINE = MergeTreeORDER BY(PostTypeId, postId);
-- edge CreatedCREATE TABLE CREAETED( from_user UInt64, to_post UInt64,) ENGINE = MergeTreeORDER BY(from_user, to_post);Edge Indexes (WIP)
Section titled “Edge Indexes (WIP)”Work is underway on edge indexes using materialized views and bitmaps to improve both storage efficiency and traversal performance.
Use ADJ INDEX when creating a bitmap index on an edge. Currently, bidirectional indexes are created by default, but once the feature matures, the API will support unidirectional indexes.
CREATE REL TABLE CREATED(From User To Post, ADJ INDEX(true));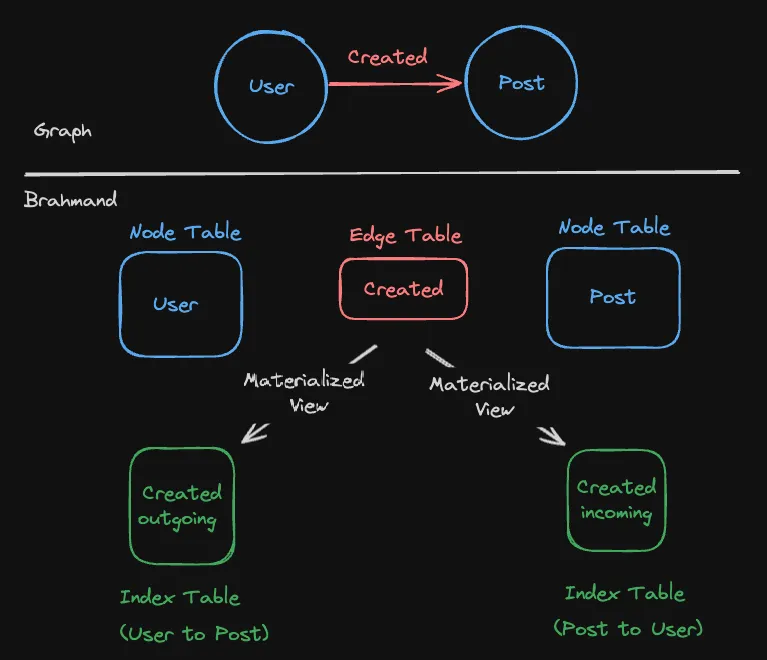
-- edge index - Created outgoing directionCREATE TABLE CREAETED_outgoing( from_id UInt64, to_id AggregateFunction(groupBitmap, UInt64)) ENGINE = AggregatingMergeTreeORDER BY from_id;
-- MV for outgoing edgeCREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv_CREAETED_outgoing TO CREAETED_outgoing ASSELECT from_user AS from_id, groupBitmapState(to_post) AS to_idFROM CREAETEDGROUP BY from_id;
-- edge index - Created incoming directionCREATE TABLE CREAETED_incoming( from_id UInt64, to_id AggregateFunction(groupBitmap, UInt64)) ENGINE = AggregatingMergeTreeORDER BY from_id;
-- MV for incoming edgeCREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv_CREAETED_incoming TO CREAETED_incoming ASSELECT to_post AS from_id, groupBitmapState(from_user) AS to_idFROM CREAETEDGROUP BY from_id;Bitmap-Based Edge Index Storage
Section titled “Bitmap-Based Edge Index Storage”Edges are stored using ClickHouse’s Roaring Bitmap (via AggregateFunction(groupBitmap, UInt64)), offering:
-
High compression of large integer sets
-
Fast set operations for union/intersection during traversals (WIP)